Google Analytics is an essential tool for any company that wishes to track the effectiveness of its internet marketing campaigns. Inbound Marketing has proven to be a very effective method of marketing and as such, it is only natural that a solution should be available that combines the two. That solution is called Google Analytics.
Experts of the leading SEO company in Mumbai explain that setting up Google Analytics is not a particularly difficult task, but it does require you to follow some basic guidelines so that the tracking on your website for visitors works correctly, regardless of whether the visitors are human or from search engines. These simple steps will ensure that your Google Analytics account will begin picking up valuable data. Additionally, Google Analytics can provide insight into who is visiting your website, where they are coming from, and what they are doing when they get to your website.
Table of Content
- What is Google Analytics?
- What is the use of Google Analytics?
- Create an account
- Setting up Google Analytics for your website takes just a few easy steps.
- Adding New Views
- Set up your site’s Analytics tag.
Key Takeaways
- Google Analytics is a free web analytics service offered by Google that tracks and reports website traffic.
- It allows website owners to measure how visitors arrive at their site and how much time they spend there.
- Google Analytics is a powerful tool for tracking the effectiveness of internet marketing campaigns.
- Views in Google Analytics can be set up to filter traffic by different criteria.
- Views can be edited to change the view name, time zone, site search parameters, and other settings.
- To add a new view to your account, go to the admin section of your Analytics account, then select “Views,” and click the “Add new View” button.
What is Google Analytics?
What is Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is Google’s web analytics service. Google Analytics was created in 2005 when Google purchased Urchin Software, which developed a website tracking service established in 1997 by WebTrends. In 1997, Michael Seo developed the code that powers Urchin Software.
It’s a free web analytics service offered by Google that tracks and reports website traffic. Google Analytics customers can use a dashboard to visualize data and better understand how users engage with their websites by viewing reports of the most popular content, popular visitors, geographical data, mobile usage, and more.
It was created in 2005 to help website owners measure how visitors arrived at their site and how much time they spent there. In 2006, Google launched website conversion tracking, which tracked whether site visitors made purchases or performed another desired action.
Professionals of any top Digital Marketing Agency in Mumbai employ this tracking application as it is free to use and provides real-time analysis with detailed information on how visitors interact with web pages. The services are used for collecting data on visits, page views, and new users. Data collected includes information on visitor IP addresses and browser types as well as referring pages and search engine keywords used to locate the site.
The site also offers information on how visitors got to its site, what they click on while there, how long they stay, and if an ad or search brought them there. This can be useful in understanding what content visitors find interesting or not interesting enough to view.
Web analytics are used to measure:
There are four components of an effective web analytics program:
- page views —how often each page or resource is viewed;
- visitor behaviour —which areas of the site are most popular;
- traffic sources — where visitors come from; and
- advertising effectiveness
What is the use of Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is a free service that allows you to track your website’s traffic and improve your SEO. It’s used to collect and analyze data about visitors to a website and hence is used and recommended by the experts of the best SEO company in Mumbai.
There are many different ways to use the information collected by Google Analytics. You might want to know:
- Which pages have the most visitors?
- What search terms do they use?
- What are they looking for on your site?
- Where in the world do they come from?
- What websites or search engines referred them to you? Which pages did they visit right before and right after they visited you?
- How long do they stay on your site?
- Are they new visitors to your site?
- Do they like what they see and come back often, or do they leave quickly?
- How much traffic does your site get?
- Which pages are the most popular, or where is it concentrated (just a few popular pages, or is it distributed throughout the site)?
- How many new and returning visitors do you get each day/week/month/year?
- How does that compare with this time last year, or last month/week/day?
- Are you getting fewer visitors now than earlier this year?
Use of Google Analytics
How did people find your website – from a search engine, an ad, an email link or banner, a link from another website, etc.? All of your questions can be answered by Google Analytics.
Now that you know WHY you need it, let’s see HOW to use it.
For that, first, create an account on it.
Creating a Google Analytics an account
Google Analytics Setup Steps
To get started using Google Analytics, follow these steps:
- To begin using Google Analytics, sign up for a Google Account if you don’t already have one.
- Get your Analytics account set up or sign in to it.
Choose one of the following:
- To create an account you need to click on Start for free.
- If you already have an account then click on Sign in to Analytics.
Setting up Google Analytics for your website takes just a few easy steps.
After you’ve created a Google Analytics account for your website, you can create a property for that website. For example, if you want to view data for this website but the website is affiliated with a different business than the one that owns your Google Analytics account, you can create an additional property in your Google Analytics account.
- In the Admin section, click Create Account.
- Provide your Google Analytics account name. Select a time frame for the data you want to view and select whether you want to share that data with Google.
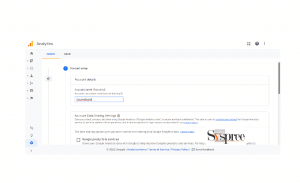
Give your account a name
- Click Next to add this property to your account.
Let’s Create the property
1. Give your property a name, choose the reporting time zone and currency, and select the day of the week to record visits. For example, if someone visits your website on a Tuesday while you’re at work, but they’re at home on their computer, Analytics will count that as a Monday visit.
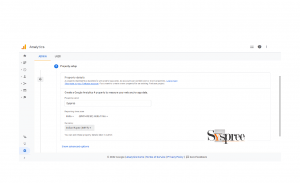
Give your property a name
- If you use Greenwich Mean Time to set your time zone, you won’t have to adjust your Analytics tracking codes if Daylight Savings Time is in effect.
- Changing the time zone of a property affects the date and time stamps of future data only. If you update your time zone, you may see a flattening or increase in data, depending on whether you shift the setting forward or backwards by an hour. After you change your time zone settings, Analytics uses the old time zone to display data for a short time.
2. In the final section of the Tracking Code box, click on the Show advanced options button and check the box next to Create a Universal Analytics property.
3. Enter your website’s domain name. Select the protocol (HTTP or HTTPS).
Use either UTF-8 or Punycode characters when naming your domain to ensure compatibility with most sites (including the WordPress.com blogging platform). Mark any in-text URLs you use with the UTF-8 character encoding so that your readers’ web browsers will be able to easily convert them into clickable links.
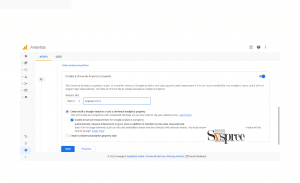
Enter the website’s domain name and select the option for both G4 and UA property
4. Let’s go ahead and set up both a Google Analytics 4 property and a Universal Analytics property.
- While Universal Analytics gives you a complete picture of your website’s traffic, Google Analytics 4 property allows you to set up a parallel account that collects data alongside your Universal Analytics property. After you add the Google Analytics tag to your website, information will be sent to both properties. To switch between properties in your Google Analytics account, you can use the property selector or the Admin screen.
- When you enable Google Analytics for your site, you get a property ID. If you want to upgrade your site’s tracking to Universal Analytics, it needs to be migrated from the current property ID to a new property ID. Migrating from one property ID to another can be accomplished with this connection.
- Create a Universal Analytics property only. If you choose this option, you’ll add Google Analytics to a Universal Analytics property.
5. Click Next and fill out the information about your business.
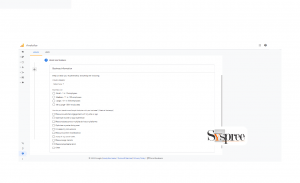
Enter your business information
6. Click the Create button.
You will be asked to accept the Google Analytics Terms of Service and Data Processing Amendment; click Accept.
Find out how to change property settings.
Changing the Property Name, Industry Category, and Advertising Features on your site requires updating your Google Analytics account.
To change property settings, you need the Editor role.
1. Sign in to your Google Analytics
2. To get started, go to the Admin tab, select the property you want to edit, and then click View.
3. To edit your property settings, click Property Settings and edit any of the following:
- Property name: The name that appears in Analytics.
- Default URL: The default URL for the property is http://example.com.
- Default View: Default view for when data is taken from Analytics
- Industry Category: What industry-vertical category best represents your website?
- Advanced Settings: Choose whether you want to have manual tagging override auto-tagging for Google Ads and Search Ads 360 integrations, and Campaign Manager 360 and Display & Video 360 reporting integrations.
- Advertising Features: You can turn Google support for Advertising Features on or off.
- Get Google Play Developer Console Data: You can see Google-Play performance information about your apps that you have published to Google Play in Analytics. If you want to see this data, check the box.
- iOS Campaign Tracking: Turn on campaign tracking to measure in-app campaigns. Use custom URLs for better reporting.
- In-Page Analytics: Enable or disable data sharing between Analytics and the website publisher. Open the Google Analytics In-Page Analytics report in embedded mode or full mode.
- Search Console Settings: Connect Search Console data with Analytics.
- User Analysis: Turn this setting on to add the “Users” metric to standard reports. Learn how Google Analytics calculates the “Users” metric.
4. Now click on Save.
To delete a property
To move a file to the Trash, press Command+Delete, you must have the Editor role and be using the Editor view. When you move a property to the Trash Can, all of its component views are also moved to the Trash Can. Move the file to the Trash to delete it.
- Sign in to your Google Analytics
- Click on Admin, and then select the property you want to Delete.
- To delete your property go to Property Settings.
- Select Move to Trash Can.
- Click on Move to Trash Can in the confirmation screen.
Adding New Views
Google Analytics Views helps you understand your website traffic. Here’s how to set it up.
Step 1: Set up a new view for an existing property.
Here’s how to Set up a new view in your account. This will give you the ability to filter traffic by different criteria:
- Go to the admin section of your Analytics account, then select “Views”:
- Then click the “Add new View” button:
- You’ll be asked to give your new view a name. I’ve called mine “UK only”, but you can call it anything you like:
- Then you with get a blank screen where you can start adding filters and segments. Feel free to jump ahead and create your new view now; you can always add filters or segments later if you want to.
Step 2: Choose which device types you want to include in your new view.
Below the list of views, you’ll see an option called “Includes”. Click on that:
Now you will have a list of options for filtering by different types of devices:
I’ve selected “Desktop” and “Tablet”.
Step 3: View reports in the time zone of your choice.
If you link your Google Analytics and Google Ads accounts, the time zone setting is automatically set to your Google Ads preference.
How Does Reporting Time Zone Work?
- The time zone setting only affects how data appears in your reports, not how you collect it. Setting your Analytics profile’s time zone to Pacific Time adjusts start and end times shown in reports according to Pacific Time, even if you have sessions originating in New York, London, or Moscow.
- If you select a time zone that changes for Daylight Savings Time, the Analytics program will adjust for it automatically. If you want to use Greenwich Mean Time instead of your local time zone, make sure you click this link.
- A change in time zone will not affect historical data, but you might see a flat spot or spike in your reports as the new time setting is applied to your data. Your reports might also refer to the old-time setting for a short period after you update this setting.
Step 4: To create a User ID view(Only for User ID enabled Properties ), click the toggle ON icon. To create a reporting view, leave the toggle set to OFF.
Step 5: Click on Create View and it’s Done.
Remember,
The maximum number of views you can add to a property is 25.
Now that you know how to Create a View let’s see how to Edit a view.
How to Edit Your View Settings
Once you create a view, you can edit its settings. Note that some of these settings are available only for web properties and not for app properties. If you’re editing a view within an app property, the options below don’t appear.
Remember:
To edit view settings, you need the Editor role.
To change view names, time zone, Site Search parameters, and other settings, follow these steps:
Step 1: Sign in to your Google Analytics.
Step 2: Click on Admin, and then select the view you want to edit.
Step 3: Within the View Column, select View Settings.
Step 4: Some general information
- View Name: This is the name that appears in the list of views.
- Website’s URL: To add Google Analytics tracking code to your web pages, please provide the domain names of your web pages in the box below.
- Time zone country or territory: The time zone setting only affects how data appears in your reports, not how you collect it. Your reports might also refer to the old-time setting for a short period after you update this setting.
If you select a time zone that changes for Daylight Savings Time, the Analytics program will adjust for it automatically. If you want to use Greenwich Mean Time instead of your local time zone, make sure you click this link.
A change in time zone will not affect historical data, but you might see a flat spot or spike in your reports as the new time setting is applied to your data. Your reports might also refer to the old-time setting for a short period after you update this setting.
- Default page: The page a visitor sees when they navigate to your site via a web browser, enter www.example.com into their browser window, and press the enter key. Enter the filename of your default page in this field —usually index.html or default.html.
Enter a name to help you identify the page in your reports. This will help you differentiate between pages with similar titles or for internal use only URLs.
- Exclude URL Query Parameters: If you want to exclude any query parameters or unique session IDs from reports, enter them as a comma-separated list.
Complete this field with uppercase and lowercase letters. Keep it under 2048 characters.
Please be sure to identify query parameters here as they appear in the original, unfiltered URIs. It is tempting to apply filters, then go back to the setting to identify query parameters as they appear in your filtered reports. However, this ignores the case-sensitive requirement of this setting.
- The currency that you will see will be: (USD, JPY, EUR, etc.)
- Bot filtering: This option lets you exclude sessions from known bots and spiders.
Step 5: Site Search: Create a Site Search.
Site Search gives you insights into how your visitors used the search function to find information on your site, which terms they used, and how your search results increased their engagement with your site.
You must set up Site Search for each reporting view that you want to report on user search activity. To do so, follow these steps:
- Sign in to your Google Analytics.
- Click on Admin, and then select the view you want to edit.
- Within the View Column, select View Settings.
- Under Site Search Settings, set Site Search Tracking to ON to track what people are searching for on your website.
- In the Query Parameter field, enter all of the search terms that identify your internal search parameters. If a query parameter is chosen by just a single letter, enter it exactly as it appears. If multiple query parameters are selected by only one or two letters each, use an underscore between them: like q_a. Remember not to enter anything other than letters in this field. Enter up to five sets of query parameters in this field, separated by commas. Do not add any additional letters or characters at the end of each string of letters.
- Do you want Analytics to remove the query parameters from your URLs? Removing the query parameters can make it harder for Google to know how many people visit.
- When you set up site search categories, you can turn them on or off. If your site lets users refine their searches, you may want to include that feature in reports. If your users refine their search to laptops after searching for Chromebooks, the site-search URL looks something like …?q=chromebook&sc=laptop.
When you turn off categories, you are Done. Click Save.
But what if you turned it ON
- Enter a word that indicates an internal search category, such as “cat, QC, or sc”. Don’t enter the word the. For example, do not enter “sc=”, but rather just put in “sc”.
- Do you want Analytics to remove category parameters from your URLs?
Note that this will not strip any parameters from a URL you have not explicitly named. To strip all parameters, use the exclude URL Query Parameters method. This will have the same effect as banishing them from your master reporting view.
- Now click on Save
Step 6: Click on Save to save the changes you have made.
How to create a copy of the view?
It’s a good idea to create copies of your views before making data changes. You can associate multiple views with a property so that you can maintain the integrity of your data while customizing it for specific reporting purposes. For example, you might want to view the default report of sessions (the original view) and then apply a filter to see only German traffic.
You can set up multiple views for a property so that you can use the default reporting and then add customized filters. For example, you might want to view the default report of sessions and then apply a filter to see only German traffic.
-
Sign in to your Google Analytics.
-
Click on Admin, and then select the view you want to edit.
-
Within the View Column, select View Settings.
-
Click on Copy view
-
Give it a name
-
Now, Click on Copy view, and you have created a copy.
How can you Delete a View?
An important thing to know is that once a view is “trashed” (moved to the Trash Can), it is permanently removed after 35 days and can no longer be retrieved. This includes any setting and configuration preferences (like Goals) but not data saved at the property or account levels.
To move a view to the Trash Can, be sure you have the Editor role. Then:
-
Sign in to your Google Analytics.
-
Click on Admin, and then select the view you want to edit.
-
Within the View Column, select View Settings.
-
Select Move to Trash Can.
-
Click on Trash view to confirm.
Set up your website’s Analytics tag.
Basic instructions
1. As a first step, you need to create a Google Analytics property for each website you want to track.
When you create a new website property, Google Analytics automatically creates a Tracking ID and a global site tag. In Google Analytics, click Admin, and navigate to the Tracking Info section under PROPERTY SETTINGS.
You can find your Tracking ID and the global site tag on the Google Analytics Settings page. See the following section for more detail.
2. To track visitors to your website through Google Analytics, you must paste the site tag into the <head> section of every web page that you want to track.
Find your Google Analytics Tracking ID and global site tag.
-
Sign in to your Google Analytics
-
Click on Admin
-
Pick an account from the drop-down menu in the ACCOUNT column.
-
In the PROPERTY section, select a property.
-
Under PROPERTY, click TRACKING INFO and then insert your tracking code.
Your Google Analytics ID is visible between two dashes at the very top of this document.
Your the global site tag code; it’s under Website Tracking > Global Site Tag (gtag.js).
The global site tag
The <code>site tag</code> is a line of code that you will need to insert into the head of each page on your website to track their collective data with Google Analytics.
How to add the global site tag to your web pages:
- Copy everything from the text box.
- Paste the code below after the opening <head> tag on each page where you want to track data.
Based on your site type, set up data collection.
When you use Analytics, the kind of data that’s collected depends on the type of website you want to analyze.
For Static Website
Permanent web pages do not generate HTML using a programming language or interface like Python or PHP. To collect data, you must copy and paste the Google Analytics tracking code on every page you want to measure.
- Find the <a href=”http://www.google.com/support/analytics/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=1000167″>global site tag</a> for your property and copy the code below exactly as is it.
- Paste your code (unaltered) in the <head> section of each page on your site.
For Dynamic Page
Dynamic websites generate HTML using a programming language or scripting interface. The site tag is a small snippet of code that helps Google collect data. You can include global tags and other tags on pages with different needs.
- Find your property’s global site tag, and copy it exactly.
- Place your site tag in its file.
- Link the analytics include file to your header so the snippet appears on every single page you want to measure.
If you use PHP
- Find your property’s global site tag, and copy it exactly.
- Place your site tag in its file with the name “analyticstracking.php”.
- On each page using a PHP template put the analyticstracking.php file.
- Use the following code on each template page, immediately after the opening <body> tag.
<?php include_once(“analyticstracking.php”) ?>
Note that dynamic websites can be more efficiently updated using Google Tag Manager.
Check to see that the Google Analytics site tag is working on your site.
After adding the Analytics tag to your template, visit your website to see the tag at work. Check the Real-Time reports in Analytics to see that your visit was registered.
Google tag Assistant could also help you by verifying your tag.
Conclusion:
Now that we understand how essential Google Analytics is to the Search Engine Optimization process, waste no time in taking advantage of this tool to strengthen your internet marketing campaign. Also, go through our detailed blog on Page Speed and SEO to bolster your website’s search engine results.








Thank you for sharing the information regarding setting up google analytics step by step. It helps us collect data on visits, page views, and new users.
Hi Esha, we are glad you liked our blog. Our latest blog highlights techniques to gain more leads and increase website traffic, please feel to check it out.
Thank you for sharing the blog. It helps to understand the Google Analytics setup completely. SySpree is doing a great job as a digital marketing agency in Mumbai by sharing an informative blog.
Thank you for your kind comment on our blog.
I didn’t know there were so many steps to follow to set up google analytics. Thanks, Team, now I am aware of the steps and how to use them. It made it easy for me to set up my google analytics account for my business. Thanks, once again!
We are glad to know that our blog was informative and useful for you. Do check out our recent blog: Title Tag 2022: Everything You Need To Know About Title Tags